What is new, cool and bad in Windows Server 2012R2 Essentials? I have my personal top 10 opinion. I don’t want to write only good thinks, because the administrator must know also the dark side of a product. Here is my list:
- Virtualization rights – Server 2012R2 Essentials license include virtualization rights that are different form normal, standard product. These rights include the virtualization 1 + 1. To be more specific, you don’t need to buy an additional license for the host server (if you want to have GUI), but you have to buy it for any additional VM. This will be useful for providing DR scenario in small companies with Hyper-V replica (for example to do it in our datacenter).
- AD Groups – Finally! Microsoft realizes, that user-by-user permissions are not a good approach even in small environments (especially in version 2012, where you were able to translate product to the standard version…). Now we can create groups directly in Dashboard and we can assign permissions to groups and add users to them. It’s fine. Like in the good, old SBS.
- Essentials role in standard server – Microsoft adds Essentials role to standard products in the way, that if you buy Windows Server 2012R2 Standard or Datacenter edition, you will be able to install the Essentials role. This role will give an opportunity to use Dashboard, Remote Web Workplace and other Essentials functionality. You will be able to use one or more Essentials functionalities, but in some cases, you will be limited with a limit of 100 users (for example in client backups – another good point to limit usage!).
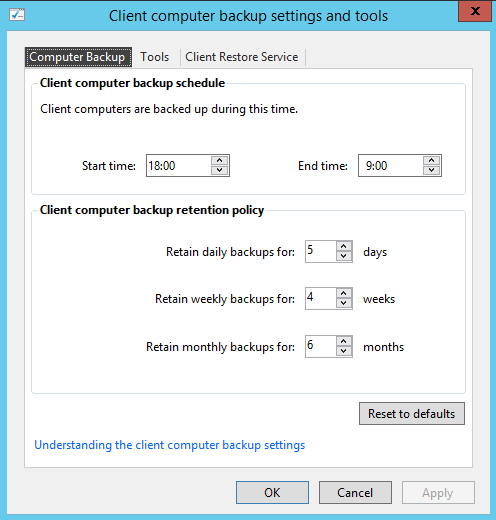
- Client computer backups – Good practice in small companies where you have users, that just use “Save” button and don’t matter where the data is going. This happens in many small companies and no one knows where the data is. In this cases, you have to backup all the environment, including client computers. Very useful functionality.
- Azure Backup – We talk again about small businesses. In many cases, the server is located under the table, security is something that they don’t think about and their data are exposed to high risk. Azure backup in those cases is a very good functionality to store crucial company data in a secure location. Of course, this is not a replacement for the normal server backup. We still need to backup our server, because Azure backup will not protect you against accidents like hardware failure or similar. In these cases, you will need a local backup to restore the server quickly.
- Remote Web Workplace – One of my favorite functionalities in Essentials or old SBS server. I use this functionality a lot, I talk a lot about it, but is still buggy. I mentioned this bug in my blog previously and I reported this bug to Microsoft when SBS 2011 public preview was released. From than the bug is still present, so be careful who will have the Administrator rights in your system. It is not really a good point to preserve private data.
- Internal “local” domain – by default is no chance to change FQDN domain from .local to any other domain name. This will be not smart after January 1st, when you will not be able to add local domain to trusted certificates and in many cases this is not a good idea to do it this way. The only way to move away from local domain is installing the Essential role with PowerShell (Break the Essentials wizard and run Start-WssConfigurationService -CompanyName “ContosoTest” -DNSName “ContosoTest.com” -NetBiosName “ContosoTest” -ComputerName “YourServerName” –NewAdminCredential $cred -Setting All from elevated PowerShell).
- Windows Phone and Windows 8 App – Both apps are present from version 2012, but I think, that is a nice approach to have easy access to all data on the server. It is also nice for administrators with quick status report for network. Nice thing.
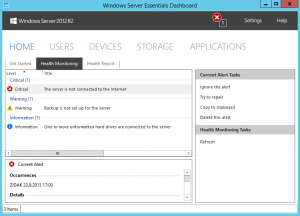
- Health Monitoring and reports – Another thing, that make SBS and Essentials servers popular and easy to manage. Very nice idea to have all events reported on the same screen. In this version is improved with some knowledge results for every error or warning. It is very useful for administrators. The other good functionality of Health monitoring is that it can send E-Mails with health reports and critical errors. One thing I would correct here is the schedule for generating reports; I would like these reports to be generated weekly, not hourly or daily. If you are administrator for more servers, there are too many mails with current configuration.
- Launchpad – Nice application for not so expert users. I think that is very good to advice all users in small companies to use it, because it has a lot of good shortcuts. The first one is access to all shared folders on server without mapping them. This will solve administrator problems like “I cannot see Y drive”. The second nice thing is the list of errors and warnings; including disk space and update warnings. And the last, but not least, is the backup functionality. Unfortunately it is not so good, because a non administrator user can backup his machine, but he is unable to restore some files. This could be corrected.
I hope, that this list will give you a good opinion about this server. Honestly is not a bed product and it is very useful and easy to manage. It is dedicated to small companies and it is made with this logic. Consider it, test it and use it. You will be satisfied with it!.
